Whether you are installing a solar panel on a flat roof or a pitched roof the output of the solar pv system would be increased by optimizing the tilt angle.
Angle of incidence specs for solar panels.
Orientation of the panels.
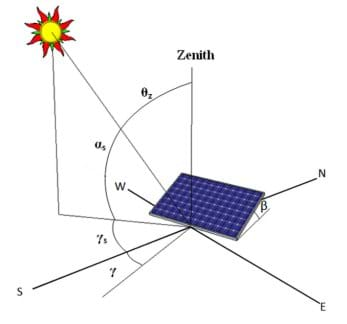
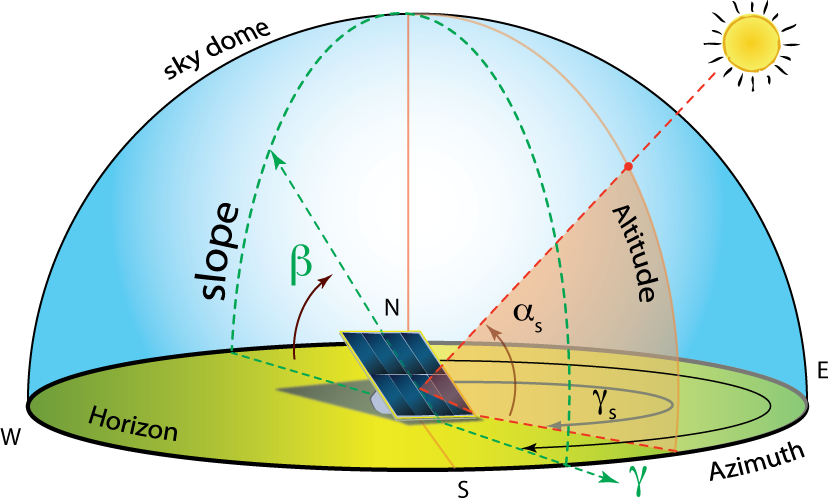
The complement of this angle is the zenith angle θ z that is defined by the vertical and the line to the sun i e the angle of incidence of beam radiation on a horizontal surface.
Elevation angle and azimuth angle commonly shortened to angle and azimuth for brevity.
This decline is due to the fact that solar panels during most of the day are exposed to weak and not perpendicular sunlight.
At 90 from true south therefore east and west production can drop to 30.
The surface azimuth angle at describes the deviation from the south.
The vertical tilt of your panels.
Today we re going to explain how to mount your solar panels to get the most energy from them.
This is the angle between the line that points to the sun and the angle that points straight out of a pv panel also called the line that is normal to the surface of the panel.
While the angle of your solar panels is important a more important factor in your energy production is going to be the direction your panels face.
However if the panels are turned at an angle greater than 45 compared to true south production begins to decrease significantly.
Solar azimuth angle a.
Angular displacement from south of the projection of beam radiation on the horizontal plane.
Let s start with two key terms.
The calculation of the angle of incidence 0tilt on a tilted surface is more complicated.
This is the most important angle.
This is because the sun is always in the southern half of the sky in the northern hemisphere.
This angle is also called the zenith angle dz.
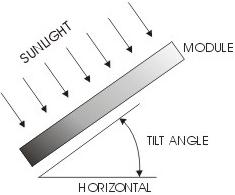
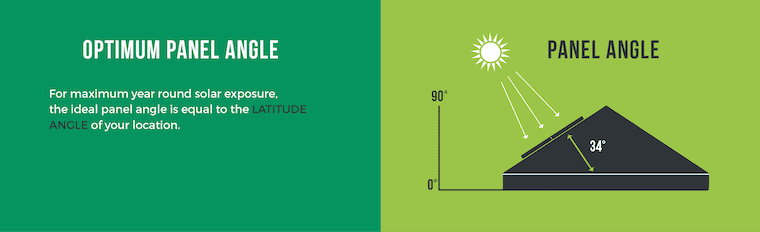
The array s tilt is the angle in degrees from horizontal.
A flat roof has a 0 degree tilt and a vertical wall mount has a 90 degree tilt angle.
Solar panels are most efficient when pointing at the sun so engineers want to minimize this angle at all times.